Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiology
TechnologyIndustry
Events
Webinars

- Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
- Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
- Existing Hospital Analyzers Can Identify Fake Liquid Medical Products
- Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
- New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
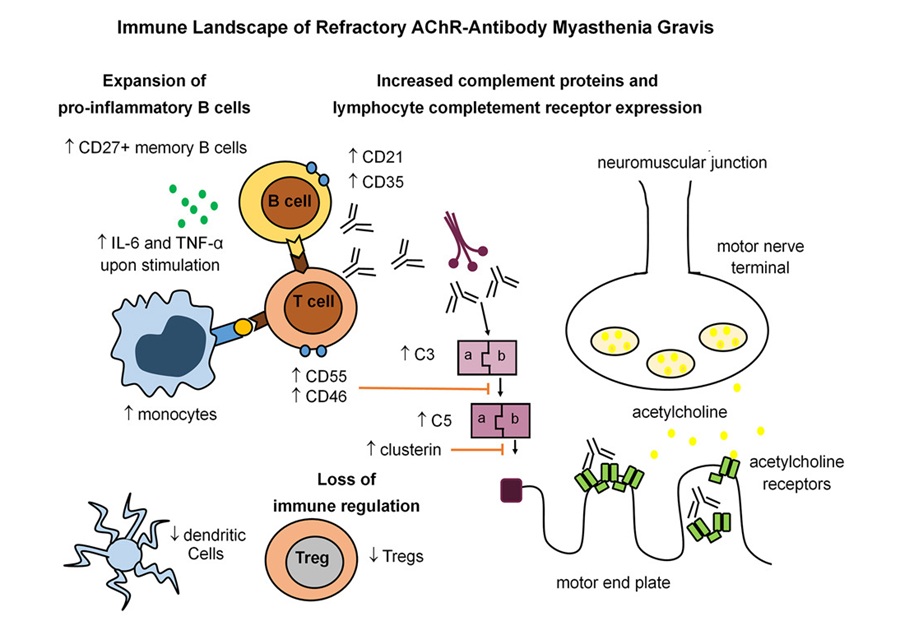
- Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
- New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
- WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
- New Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
- AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
- Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples

 Expo
Expo
- Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
- Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
- Existing Hospital Analyzers Can Identify Fake Liquid Medical Products
- Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
- New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
- New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
- WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
- New Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
- AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
- Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples