Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Webinars

- Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
- Study Compares Analytical Performance of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Assays
- Blood Test Could Predict and Identify Early Relapses in Myeloma Patients
- Compact Raman Imaging System Detects Subtle Tumor Signals
- Noninvasive Blood-Glucose Monitoring to Replace Finger Pricks for Diabetics
- Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
- “Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
- Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
- Two-in-One DNA Analysis Improves Diagnostic Accuracy While Saving Time and Costs
- Newly-Identified Parkinson’s Biomarkers to Enable Early Diagnosis Via Blood Tests
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
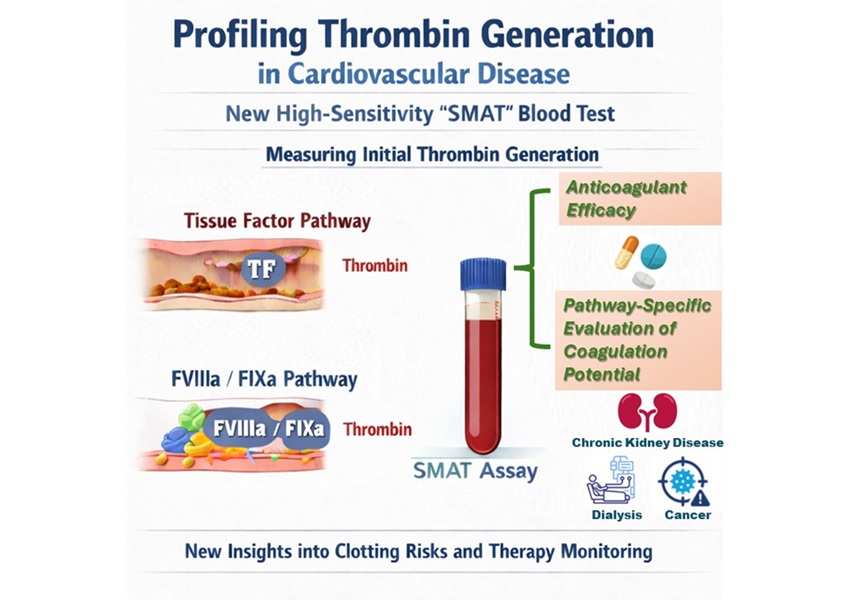
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
- AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
- Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
- WHX Labs Dubai to Gather Global Experts in Antimicrobial Resistance at Inaugural AMR Leaders’ Summit
- BD and Penn Institute Collaborate to Advance Immunotherapy through Flow Cytometry
- Abbott Acquires Cancer-Screening Company Exact Sciences
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
- AI Algorithms Improve Genetic Mutation Detection in Cancer Diagnostics
- Skin Biopsy Offers New Diagnostic Method for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Fast Label-Free Method Identifies Aggressive Cancer Cells
- New X-Ray Method Promises Advances in Histology

 Expo
Expo
- Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
- Study Compares Analytical Performance of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Assays
- Blood Test Could Predict and Identify Early Relapses in Myeloma Patients
- Compact Raman Imaging System Detects Subtle Tumor Signals
- Noninvasive Blood-Glucose Monitoring to Replace Finger Pricks for Diabetics
- Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
- “Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
- Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
- Two-in-One DNA Analysis Improves Diagnostic Accuracy While Saving Time and Costs
- Newly-Identified Parkinson’s Biomarkers to Enable Early Diagnosis Via Blood Tests
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
- AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
- Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
- WHX Labs Dubai to Gather Global Experts in Antimicrobial Resistance at Inaugural AMR Leaders’ Summit
- BD and Penn Institute Collaborate to Advance Immunotherapy through Flow Cytometry
- Abbott Acquires Cancer-Screening Company Exact Sciences
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
- AI Algorithms Improve Genetic Mutation Detection in Cancer Diagnostics
- Skin Biopsy Offers New Diagnostic Method for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- Fast Label-Free Method Identifies Aggressive Cancer Cells
- New X-Ray Method Promises Advances in Histology