Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events

- Paper-Based Device Boosts HIV Test Accuracy from Dried Blood Samples
- AI-Powered Raman Spectroscopy Method Enables Rapid Drug Detection in Blood
- Novel LC-MS/MS Assay Detects Low Creatinine in Sweat and Saliva
- Biosensing Technology Breakthrough Paves Way for New Methods of Early Disease Detection
- New Saliva Test Rapidly Identifies Paracetamol Overdose
- Simple DNA PCR-Based Lab Test to Enable Personalized Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
- Rapid Diagnostic Test to Halt Mother-To-Child Hepatitis B Transmission
- Simple Urine Test Could Help Patients Avoid Invasive Scans for Kidney Cancer
- New Bowel Cancer Blood Test to Improve Early Detection
- New Method Rapidly Diagnoses CVD Risk Via Molecular Blood Screening
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Test for Fetal RhD Status Demonstrates 100% Accuracy
- WBC Count Could Predict Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms
- New Platelet Counting Technology to Help Labs Prevent Diagnosis Errors
- Streamlined Approach to Testing for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Improves Diagnostic Accuracy
- POC Hemostasis System Could Help Prevent Maternal Deaths
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Test Predicts Dangerous Side Effect of Cancer Treatment
- New Test Measures Preterm Infant Immunity Using Only Two Drops of Blood
- Simple Blood Test Could Help Choose Better Treatments for Patients with Recurrent Endometrial Cancer
- Novel Analytical Method Tracks Progression of Autoimmune Diseases
- 3D Bioprinted Gastric Cancer Model Uses Patient-Derived Tissue Fragments to Predict Drug Response
- Innovative ID/AST System to Help Diagnose Infectious Diseases and Combat AMR
- Gastrointestinal Panel Delivers Rapid Detection of Five Common Bacterial Pathogens for Outpatient Use
- Rapid PCR Testing in ICU Improves Antibiotic Stewardship
- Unique Genetic Signature Predicts Drug Resistance in Bacteria
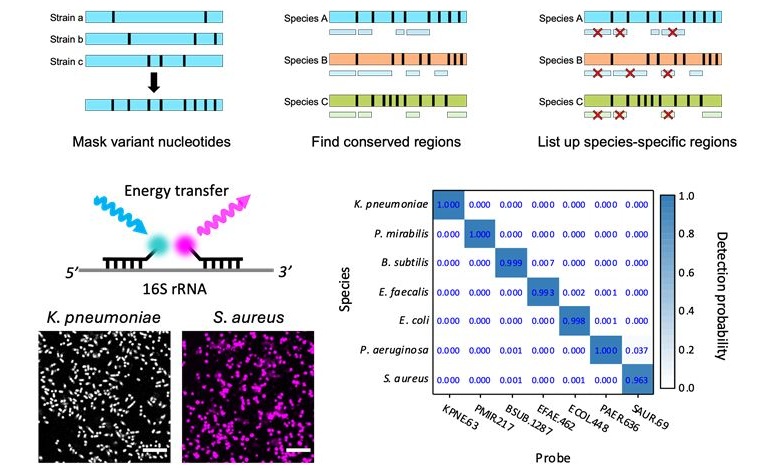
- Unique Barcoding System Tracks Pneumonia-Causing Bacteria as They Infect Blood Stream
- Novel Sensor Technology to Enable Early Diagnoses of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disorders
- 3D Printing Breakthrough Enables Large Scale Development of Tiny Microfluidic Devices
- POC Paper-Based Sensor Platform to Transform Cardiac Diagnostics
- Study Explores Impact of POC Testing on Future of Diagnostics
- Low-Cost, Fast Response Sensor Enables Early and Accurate Detection of Lung Cancer
- Grifols and Inpeco Partner to Deliver Transfusion Medicine ‘Lab of The Future’
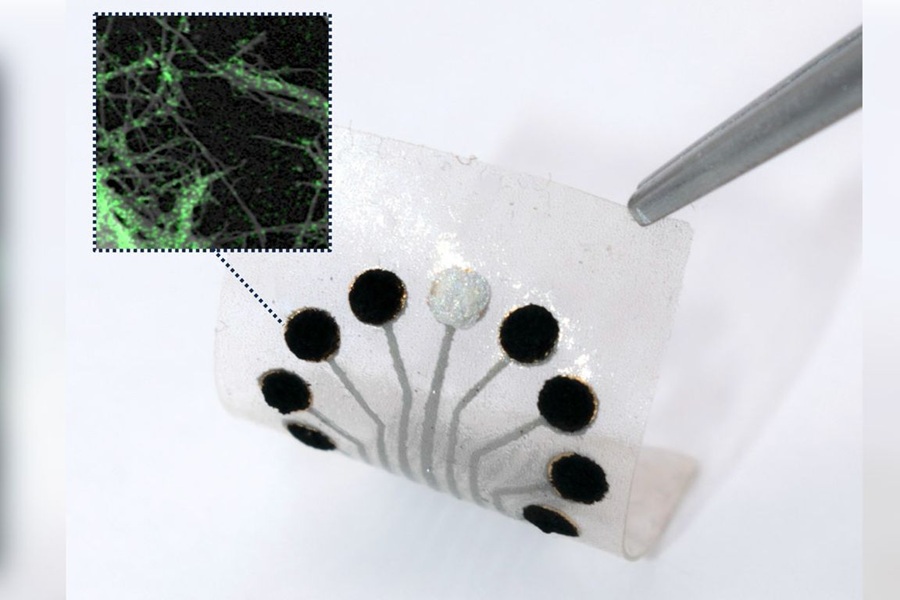
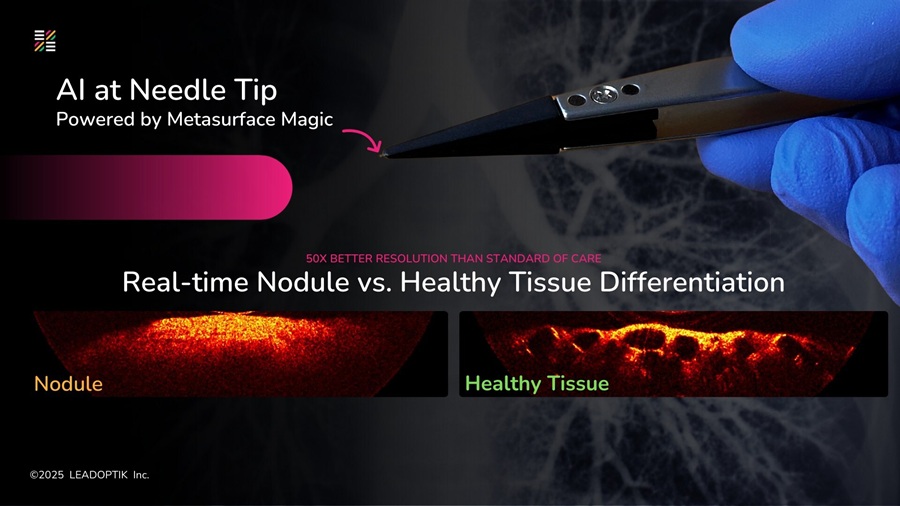
- Research Collaboration to Advance AI-Enhanced, Real-Time Optical Imaging in Lung Cancer Biopsy
- CACLP 2025 Unites Global Innovators in IVD Industry
- Bio-Rad to Acquire Digital PCR Developer Stilla Technologies
- ABL Signs Know-How License and Transfer Agreement for Siemens’ Fast Track Diagnostics PCR Portfolio
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- New AI Model Predicts Gene Variants’ Effects on Specific Diseases
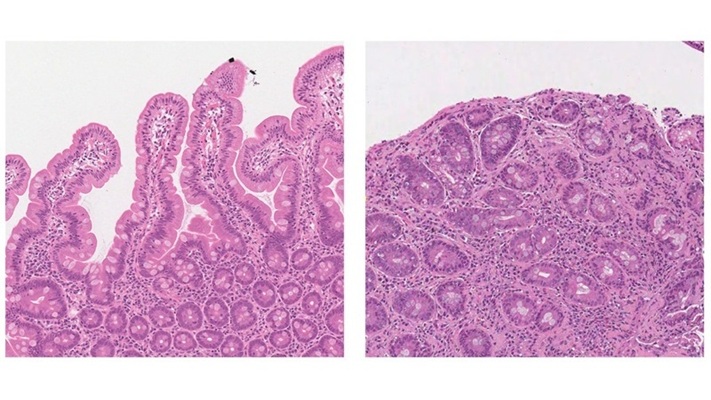
- Powerful AI Tool Diagnoses Coeliac Disease from Biopsy Images with Over 97% Accuracy
- Pre-Analytical Conditions Influence Cell-Free MicroRNA Stability in Blood Plasma Samples
- 3D Cell Culture System Could Revolutionize Cancer Diagnostics
- Painless Technique Measures Glucose Concentrations in Solution and Tissue Via Sound Waves

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us


- Paper-Based Device Boosts HIV Test Accuracy from Dried Blood Samples
- AI-Powered Raman Spectroscopy Method Enables Rapid Drug Detection in Blood
- Novel LC-MS/MS Assay Detects Low Creatinine in Sweat and Saliva
- Biosensing Technology Breakthrough Paves Way for New Methods of Early Disease Detection
- New Saliva Test Rapidly Identifies Paracetamol Overdose
- Simple DNA PCR-Based Lab Test to Enable Personalized Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
- Rapid Diagnostic Test to Halt Mother-To-Child Hepatitis B Transmission
- Simple Urine Test Could Help Patients Avoid Invasive Scans for Kidney Cancer
- New Bowel Cancer Blood Test to Improve Early Detection
- New Method Rapidly Diagnoses CVD Risk Via Molecular Blood Screening
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Test for Fetal RhD Status Demonstrates 100% Accuracy
- WBC Count Could Predict Severity of COVID-19 Symptoms
- New Platelet Counting Technology to Help Labs Prevent Diagnosis Errors
- Streamlined Approach to Testing for Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Improves Diagnostic Accuracy
- POC Hemostasis System Could Help Prevent Maternal Deaths
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Test Predicts Dangerous Side Effect of Cancer Treatment
- New Test Measures Preterm Infant Immunity Using Only Two Drops of Blood
- Simple Blood Test Could Help Choose Better Treatments for Patients with Recurrent Endometrial Cancer
- Novel Analytical Method Tracks Progression of Autoimmune Diseases
- 3D Bioprinted Gastric Cancer Model Uses Patient-Derived Tissue Fragments to Predict Drug Response
- Innovative ID/AST System to Help Diagnose Infectious Diseases and Combat AMR
- Gastrointestinal Panel Delivers Rapid Detection of Five Common Bacterial Pathogens for Outpatient Use
- Rapid PCR Testing in ICU Improves Antibiotic Stewardship
- Unique Genetic Signature Predicts Drug Resistance in Bacteria
- Unique Barcoding System Tracks Pneumonia-Causing Bacteria as They Infect Blood Stream
- Novel Sensor Technology to Enable Early Diagnoses of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disorders
- 3D Printing Breakthrough Enables Large Scale Development of Tiny Microfluidic Devices
- POC Paper-Based Sensor Platform to Transform Cardiac Diagnostics
- Study Explores Impact of POC Testing on Future of Diagnostics
- Low-Cost, Fast Response Sensor Enables Early and Accurate Detection of Lung Cancer
- Grifols and Inpeco Partner to Deliver Transfusion Medicine ‘Lab of The Future’
- Research Collaboration to Advance AI-Enhanced, Real-Time Optical Imaging in Lung Cancer Biopsy
- CACLP 2025 Unites Global Innovators in IVD Industry
- Bio-Rad to Acquire Digital PCR Developer Stilla Technologies
- ABL Signs Know-How License and Transfer Agreement for Siemens’ Fast Track Diagnostics PCR Portfolio
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- New AI Model Predicts Gene Variants’ Effects on Specific Diseases
- Powerful AI Tool Diagnoses Coeliac Disease from Biopsy Images with Over 97% Accuracy
- Pre-Analytical Conditions Influence Cell-Free MicroRNA Stability in Blood Plasma Samples
- 3D Cell Culture System Could Revolutionize Cancer Diagnostics
- Painless Technique Measures Glucose Concentrations in Solution and Tissue Via Sound Waves