Expo
Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events

- Screening Tool Detects Multiple Health Conditions from Single Blood Drop
- Integrated Chemistry and Immunoassay Analyzer with Extensive Assay Menu Offers Flexibility, Scalability and Data Commutability
- Rapid Drug Test to Improve Treatment for Patients Presenting to Hospital
- AI Model Detects Cancer at Lightning Speed through Sugar Analyses
- First-Ever Blood-Powered Chip Offers Real-Time Health Monitoring
- Cutting-Edge Diagnostic Tool Rapidly Identifies Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- Novel Method Analyzes Genetic Variations in Families with High Incidence of Breast Cancer
- cfDNA Testing Reduces Pregnancy Risks
- Non-Invasive Biosensor Facilitates Early Kidney Disease Detection
- New High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Test Quickly Rules Out Heart Attack
- Newly Discovered Blood Group System to Help Identify and Treat Rare Patients
- Blood Platelet Score Detects Previously Unmeasured Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke
- Automated Benchtop System to Bring Blood Testing To Anyone, Anywhere
- New Hematology Analyzers Deliver Combined ESR and CBC/DIFF Results in 60 Seconds
- Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
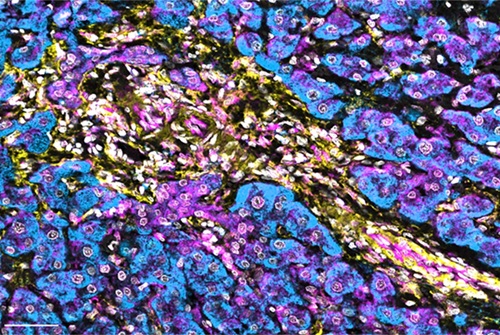
- Advanced Imaging Method Maps Immune Cell Connections to Predict Cancer Patients Survival
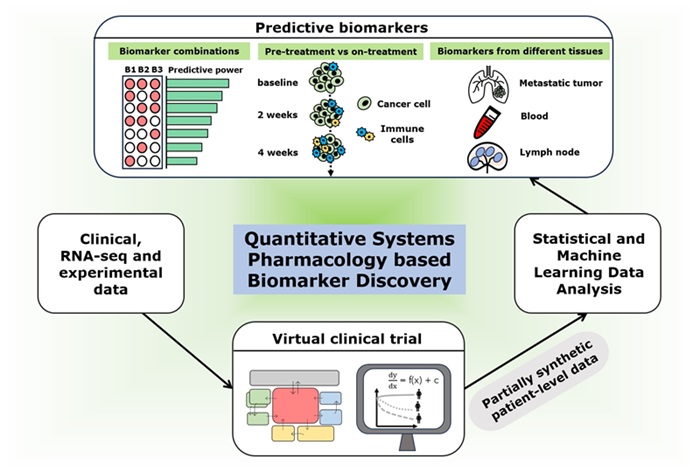
- Computational Tool Predicts Immunotherapy Outcomes for Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients
- Biomarker Could Predict Immunotherapy Response in Liver Cancer
- Epigenetic Test Could Determine Efficacy of New Immunotherapy Treatments Against Multiple Myeloma
- Blood Test Predicts Survival in Liver Cancer Patients
- High-Accuracy Bedside Test to Diagnose Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Five Minutes
- Innovative Diagnostic Approach for Bacterial Infections to Enable Faster and Effective Treatment
- Non-Invasive Stool Test to Diagnose Endometriosis and Help Reduce Disease Progression
- Automated Positive Blood Culture Sample Preparation Platform Designed to Fight Against Sepsis and AMR
- Revolutionary Molecular Culture ID Technology to Transform Bacterial Diagnostics
- New Noninvasive Methods Detect Lead Exposure Faster, Easier and More Accurately at POC
- Noninvasive Test Detects Malaria Without Blood Sample
- Low-Cost, Portable Device Detects Colorectal and Prostate Cancer in An Hour
- Light-AI Cancer Diagnosis Technology Could Eliminate Need for Traditional Blood Draws and Biopsies
- Chip-Based Blood Test Accurately Diagnoses Heart Attack in Minutes
- Beckman Coulter Partners with BioPorto for Global Distribution of Acute Kidney Injury NGAL Tests
- CACLP 2025 New Date and Venue Announced
- Roche to Develop New Diagnostic Technologies for Traumatic Brain Injuries
- LGC Clinical Diagnostics and AccuGenomics Collaborate on Enhancing Cancer Testing Accuracy
- Beckman Coulter and SphingoTec Partner to Improve Kidney Health Assessment in Critical Care
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- AI-Powered Whole-Slide Image Analyzer Predicts Immunotherapy Response for Rare Cancer Patients
- AI Tool Uses Imaging Data to Detect Less Frequent GI Diseases
- AI-Based Method Shows Promise for Pathological Diagnosis of Hereditary Kidney Diseases
- New Imaging Method Opens Door to Precision Diagnostics for Head and Neck Cancers
- Faster Measurement of Vibrational Fingerprint of Molecules to Advance Biomedical Diagnostics

Expo
 Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us
Medica
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us

 Medica
Medica
- Screening Tool Detects Multiple Health Conditions from Single Blood Drop
- Integrated Chemistry and Immunoassay Analyzer with Extensive Assay Menu Offers Flexibility, Scalability and Data Commutability
- Rapid Drug Test to Improve Treatment for Patients Presenting to Hospital
- AI Model Detects Cancer at Lightning Speed through Sugar Analyses
- First-Ever Blood-Powered Chip Offers Real-Time Health Monitoring
- Cutting-Edge Diagnostic Tool Rapidly Identifies Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- Novel Method Analyzes Genetic Variations in Families with High Incidence of Breast Cancer
- cfDNA Testing Reduces Pregnancy Risks
- Non-Invasive Biosensor Facilitates Early Kidney Disease Detection
- New High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Test Quickly Rules Out Heart Attack
- Newly Discovered Blood Group System to Help Identify and Treat Rare Patients
- Blood Platelet Score Detects Previously Unmeasured Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke
- Automated Benchtop System to Bring Blood Testing To Anyone, Anywhere
- New Hematology Analyzers Deliver Combined ESR and CBC/DIFF Results in 60 Seconds
- Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
- Advanced Imaging Method Maps Immune Cell Connections to Predict Cancer Patients Survival
- Computational Tool Predicts Immunotherapy Outcomes for Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients
- Biomarker Could Predict Immunotherapy Response in Liver Cancer
- Epigenetic Test Could Determine Efficacy of New Immunotherapy Treatments Against Multiple Myeloma
- Blood Test Predicts Survival in Liver Cancer Patients
- High-Accuracy Bedside Test to Diagnose Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Five Minutes
- Innovative Diagnostic Approach for Bacterial Infections to Enable Faster and Effective Treatment
- Non-Invasive Stool Test to Diagnose Endometriosis and Help Reduce Disease Progression
- Automated Positive Blood Culture Sample Preparation Platform Designed to Fight Against Sepsis and AMR
- Revolutionary Molecular Culture ID Technology to Transform Bacterial Diagnostics
- New Noninvasive Methods Detect Lead Exposure Faster, Easier and More Accurately at POC
- Noninvasive Test Detects Malaria Without Blood Sample
- Low-Cost, Portable Device Detects Colorectal and Prostate Cancer in An Hour
- Light-AI Cancer Diagnosis Technology Could Eliminate Need for Traditional Blood Draws and Biopsies
- Chip-Based Blood Test Accurately Diagnoses Heart Attack in Minutes
- Beckman Coulter Partners with BioPorto for Global Distribution of Acute Kidney Injury NGAL Tests
- CACLP 2025 New Date and Venue Announced
- Roche to Develop New Diagnostic Technologies for Traumatic Brain Injuries
- LGC Clinical Diagnostics and AccuGenomics Collaborate on Enhancing Cancer Testing Accuracy
- Beckman Coulter and SphingoTec Partner to Improve Kidney Health Assessment in Critical Care
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Mast Group Introduces New MAST CARBA PAcE for Rapid Carbapenemase Detection
- DRG Instruments Demonstrates DRG:HYBRID-XL Fully Automated Lab Analyzer
- Diatron Introduces New Aquila 5Dretic 5-Part Differential Hematology Analyzer
- Alifax S.r.l. Highlights First Automated System for Bacterial Culture and Susceptibility Testing
- Erba Mannheim Showcases New Launches at MEDICA 2019
- POC System that Requires Single DNA Molecule for Rapid Detection of Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens Unveiled at MEDICA 2021
- Icomes Lab Demonstrates World's Smallest and Lightest Electronic Pipette for PCR Testing at MEDICA 2021
- Bosch Exhibits Vivalytic All-in-One Analyzer for PCR Rapid Tests at MEDICA 2021
- Co-Diagnostics Introduces Its Revolutionary Coprimer Technology at MEDICA 2021
- MGI Tech Showcases World-First High-Throughput Automated Sample Transfer Processing System at MEDICA 2021
- Biovendor Group Presents CLIA Solution for Complex Diagnostics at MEDICA 2022
- Diatron Exhibits Advanced Hematology and Clinical Chemistry Analyzers at MEDICA 2022
- Immundiagnostik AG Presents New PCR Test MutaPLEX RespiraScreen4_Diff_seqc at MEDICA 2022
- Eurotrol Presents the Future of Blood Gas Controls at MEDICA 2022
- Absology Exhibits POCT Immunoassay Analyzer with Testing Time of Five Minutes
- Absology Showcases Latest Advancements in Medical Diagnostics
- Oruba Presents State-of-the-Art Self-Operating Uroflowmeters
- Awareness Technology Exhibits Incredibly Flexible ChemWell 2 ELISA and Chemiluminescent Analyzer
- BioVendor Group Demonstrates Unique IVD Platform and Immunoblot Test
- Greiner Bio-One Highlights Magnetic 3D Cell Culture Technology
- BioVendor Group Introduces Groundbreaking Immunological Biomarker
- Getein Biotech Showcases Latest POCT Analyzers
- Fapon Highlights Innovative IVD Total Solutions and Localization Services
- Wondfo Presents Advanced Solutions in CLIA Testing and Blood Gas Analysis
- Globe Scientific Exhibits Cutting-Edge Solutions for Meeting Laboratory Needs
- AI-Powered Whole-Slide Image Analyzer Predicts Immunotherapy Response for Rare Cancer Patients
- AI Tool Uses Imaging Data to Detect Less Frequent GI Diseases
- AI-Based Method Shows Promise for Pathological Diagnosis of Hereditary Kidney Diseases
- New Imaging Method Opens Door to Precision Diagnostics for Head and Neck Cancers
- Faster Measurement of Vibrational Fingerprint of Molecules to Advance Biomedical Diagnostics














.jpg)



.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpeg)



.jpg)
.jpg)
_1.jpg)

.jpg)




_1.jpg)